Introduction
In an era when nutrition and preventive healthcare dominate the global discourse, few vitamins hold as much historical and scientific significance as riboflavin—commonly known as vitamin B2. This water-soluble vitamin is not only essential for human health but also plays a crucial role in metabolic energy production and cellular function. Its applications, however, stretch far beyond nutrition and pharmaceuticals. Riboflavin has evolved into an indispensable compound in food fortification, animal feed, dietary supplements, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetic industries, creating a thriving global market that continues to expand at a remarkable pace.
As consumers increasingly seek nutrient-dense and functional foods, the riboflavin market finds itself at the intersection of science, wellness, and innovation. Furthermore, advancements in biotechnology, along with a growing focus on sustainable production methods, are transforming the landscape of vitamin manufacturing.
Moreover, the global emphasis on preventive healthcare—particularly after recent global health crises—has reignited consumer interest in essential micronutrients. As a result, riboflavin’s market presence has expanded significantly, driven by its multi-industry relevance and scientific credibility.
Therefore, understanding the evolution, market trends, challenges, scope, market size, and key growth drivers of the riboflavin market provides valuable insights into how this humble vitamin has become a cornerstone of global nutrition and industrial advancement.
Source: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-riboflavin-market
The Evolution of Riboflavin
Historical Discovery and Early Applications
The story of riboflavin begins in the early 20th century when scientists first identified it as a vital nutrient within the vitamin B complex. Initially termed “lactoflavin” due to its presence in milk, riboflavin was later recognized as a distinct compound responsible for essential metabolic functions. By the 1930s, researchers successfully isolated and synthesized riboflavin, ushering in an era of industrial-scale production.
Historically, riboflavin’s discovery was monumental—it provided the missing link in understanding how certain micronutrients influenced energy metabolism and cellular health. Unlike fat-soluble vitamins that could be stored in the body, riboflavin required consistent dietary intake, making its supplementation and fortification vital in preventing deficiencies such as ariboflavinosis, a condition that affects skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.
From Nutrient Discovery to Industrial Commodity
As nutritional science advanced, riboflavin’s versatility became increasingly evident. Early on, it was primarily used to treat deficiency-related disorders. However, as global food systems industrialized, riboflavin found applications in food fortification—especially in cereals, bread, and dairy products—to address nutritional gaps.
Simultaneously, the rise of pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries in the mid-20th century further expanded demand. Riboflavin became a staple ingredient in multivitamin formulations, reflecting its central role in human metabolism.
Furthermore, the compound’s characteristic yellow hue made it useful as a natural colorant in foods and beverages—a valuable bonus in an era when consumers began to prefer natural over artificial additives.
Biotechnological Advancements and Modern Production
Traditionally, riboflavin was produced through chemical synthesis, a process that was energy-intensive and environmentally taxing. However, the advent of biotechnology revolutionized production methods. Through microbial fermentation—particularly using strains like Bacillus subtilis and Ashbya gossypii—manufacturers achieved sustainable, high-yield production.
This transition not only reduced production costs but also aligned the market with global sustainability goals. As a result, modern riboflavin manufacturing combines scientific precision with environmental responsibility, marking a significant evolution from its early chemical roots to eco-friendly biotechnological production.
Market Trends Shaping the Riboflavin Industry
The riboflavin market is being reshaped by a combination of technological innovation, consumer health awareness, and industrial diversification. Understanding these evolving trends is essential for recognizing the market’s growth trajectory.
1. Rising Demand for Nutritional Supplements and Functional Foods
One of the most significant trends driving the riboflavin market is the surge in demand for functional foods and dietary supplements. As consumers become more proactive about their health, they are increasingly integrating vitamins into their daily routines.
Riboflavin, being a vital component of the vitamin B complex, supports energy metabolism, cellular respiration, and neurological health. Therefore, its inclusion in fortified foods, energy drinks, and nutraceuticals has become a key selling point for manufacturers seeking to meet consumer expectations for wellness-oriented products.
2. Growth in Preventive Healthcare Awareness
The global healthcare paradigm is gradually shifting from treatment-based models to prevention-focused approaches. Consequently, individuals are investing more in micronutrients that enhance immune function and metabolic efficiency.
Riboflavin’s role in converting carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into usable energy makes it indispensable for maintaining vitality and preventing fatigue. Moreover, as public awareness about vitamin deficiencies grows, the demand for riboflavin-enriched supplements continues to rise across all demographics.
3. Expansion in Animal Nutrition and Feed Fortification
Another key driver shaping the market is the use of riboflavin in animal nutrition. Livestock, poultry, and aquaculture industries rely heavily on feed fortified with vitamins to promote growth, improve immunity, and enhance productivity.
Given that riboflavin deficiency can cause stunted growth and reproductive problems in animals, its inclusion in feed formulations is both an economic and ethical imperative. Consequently, the rising global demand for meat, dairy, and eggs has indirectly boosted riboflavin consumption.
4. Technological Innovations in Fermentation and Production
Modern manufacturing processes are increasingly leveraging biotechnology and genetic engineering to optimize riboflavin yields. Fermentation-based production, particularly using microbial systems, has replaced traditional chemical synthesis due to its efficiency, scalability, and eco-friendliness.
Furthermore, continuous research into metabolic engineering has improved fermentation efficiency, enabling cost-effective and sustainable production. As industries prioritize low-carbon operations, biotechnological riboflavin production stands out as a prime example of green innovation.
5. Increasing Use in Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics
Beyond nutrition, riboflavin has made its way into the pharmaceutical and cosmetic sectors. In medicine, it supports treatments for migraines, cataracts, and anemia, while in skincare, it contributes to cell repair and antioxidant defense.
Additionally, pharmaceutical formulations are exploring riboflavin’s role as a photosensitizer in certain therapies, further expanding its medical relevance. Meanwhile, cosmetic brands increasingly market products containing vitamin B2 for its natural ability to enhance skin tone and cellular rejuvenation.
6. Consumer Preference for Natural and Clean-Label Products
Modern consumers are more informed than ever and seek products that are natural, transparent, and sustainably produced. As a result, riboflavin—especially when derived from fermentation—fits perfectly within the clean-label movement.
Food and supplement companies are emphasizing riboflavin’s natural origin and biological function to appeal to eco-conscious customers. This alignment between science and consumer sentiment has proven pivotal in shaping modern market strategies.
Challenges in the Riboflavin Market
Despite its growth potential, the riboflavin market faces a series of challenges that affect pricing, production, and global distribution.
1. Raw Material and Supply Chain Volatility
Like many biochemical products, riboflavin manufacturing depends on the availability and cost of substrates such as glucose and fermentation media. Any fluctuation in these raw materials can disrupt production and affect market prices.
Additionally, supply chain disruptions—whether due to geopolitical factors, trade barriers, or transportation issues—pose ongoing risks, particularly given the industry’s reliance on a limited number of major producers.
2. Stringent Regulatory Frameworks
Riboflavin production and marketing are governed by stringent health and safety regulations. Variations in international standards across food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic sectors make compliance a complex challenge for global manufacturers.
These regulations, while necessary for ensuring quality, often lead to higher operational costs and longer approval timelines, which can limit smaller producers’ competitiveness.
3. Market Saturation and Pricing Pressure
Because riboflavin is a mature market segment with several dominant producers, price competition remains intense. Manufacturers must continually innovate and differentiate their offerings to maintain profit margins, especially as synthetic and fermentation-based products compete for market share.
4. Limited Consumer Awareness in Developing Economies
In many developing nations, public awareness about micronutrient deficiencies and preventive nutrition remains limited. As a result, the potential market for riboflavin-enriched products is not fully realized. Bridging this knowledge gap through education and government-led fortification programs could unlock significant growth opportunities.
5. Stability and Formulation Challenges
Riboflavin is sensitive to light and alkaline conditions, which can lead to degradation and reduced efficacy in certain formulations. Therefore, maintaining its stability in processed foods and beverages requires technological precision, such as microencapsulation or controlled-release delivery systems.
Market Scope
The riboflavin market encompasses a diverse range of product types, applications, and regional segments, reflecting its widespread industrial utility.
By Product Type
-
Riboflavin 98% and 99% (Feed Grade) – Primarily used in animal nutrition.
-
Riboflavin 100% (Pharma Grade) – Utilized in pharmaceuticals and supplements.
-
Riboflavin 5’-Phosphate Sodium (Derivative) – Employed in advanced pharmaceutical and biochemical applications.
By Application
-
Pharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals – Tablets, capsules, injectables, and multivitamins.
-
Food and Beverage Industry – Fortified foods, beverages, and bakery products.
-
Animal Feed Industry – Poultry, livestock, and aquaculture nutrition.
-
Cosmetics and Personal Care – Skincare and haircare formulations.
-
Industrial Applications – Used as a colorant and biochemical reagent.
By Distribution Channel
-
Direct Industrial Supply
-
Retail Pharmacies
-
E-commerce Platforms
-
Supermarkets and Health Stores
By Region
-
Asia-Pacific: The dominant production hub and export base, led by China and India.
-
North America: Strong consumer base for nutraceuticals and dietary supplements.
-
Europe: Focused on sustainable sourcing and regulatory compliance.
-
Latin America: Emerging market with growing awareness of nutrition.
-
Middle East & Africa: Increasing healthcare investments and dietary fortification initiatives.
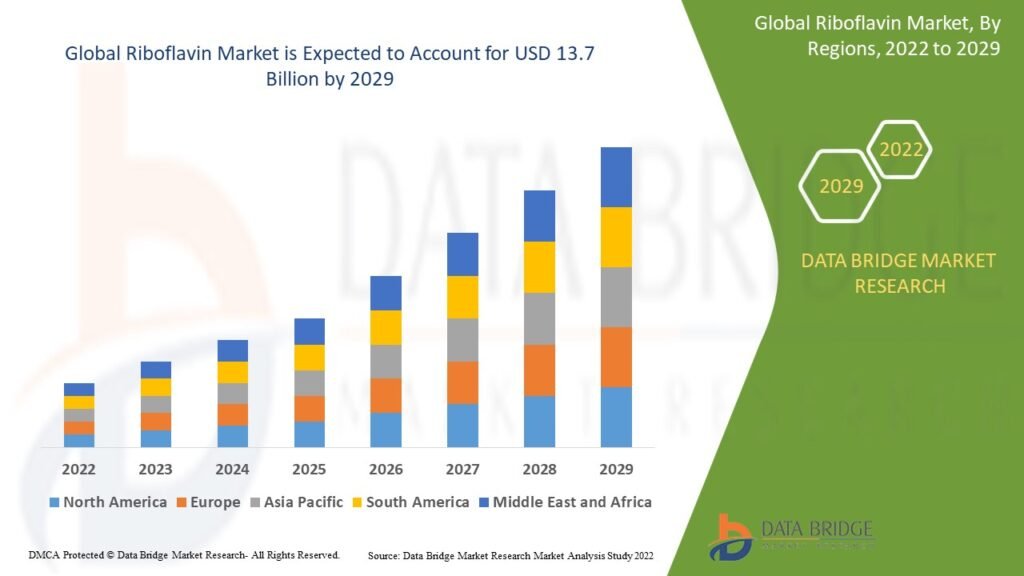
Market Size and Growth Outlook
The global riboflavin market is currently valued at approximately USD 1.4 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 2.7 billion by 2032, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 8.5%.
This growth is fueled by multiple converging factors, including rising demand for functional foods, pharmaceutical applications, and fortified animal feed. In addition, the shift toward sustainable, fermentation-based production has improved scalability while reducing costs.
The Asia-Pacific region dominates global production and export, while North America and Europe lead in innovation and end-use consumption. Meanwhile, regions such as Latin America and Africa are emerging as promising markets, driven by improving dietary standards and expanding healthcare access.
Factors Driving Growth in the Riboflavin Market
1. Increasing Global Health Consciousness
Consumers are proactively investing in nutrition to enhance their quality of life. Consequently, the demand for vitamin-enriched supplements and fortified foods continues to soar.
2. Technological Innovation in Biotechnology
Advances in microbial fermentation and genetic engineering have streamlined riboflavin production, making it more efficient, sustainable, and scalable.
3. Expanding Use in Preventive Healthcare
As public awareness of chronic diseases and nutrient deficiencies increases, riboflavin’s therapeutic role in maintaining metabolic and ocular health gains prominence.
4. Rising Animal Feed Demand
Global meat and dairy industries depend on riboflavin supplementation to maintain animal health and productivity, thereby sustaining steady industrial demand.
5. Sustainable and Green Manufacturing Practices
Eco-conscious consumers and industries increasingly prefer biologically sourced vitamins, positioning riboflavin as a leader in sustainable vitamin production.
6. Government and NGO Nutrition Initiatives
Public health campaigns promoting food fortification and vitamin supplementation—particularly in developing countries—have significantly expanded market reach.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the riboflavin market exemplifies how science, sustainability, and consumer health awareness can converge to create a dynamic global industry. From its early days as a discovered nutrient to its current status as a multi-sector industrial compound, riboflavin’s journey reflects the ongoing evolution of human health priorities and technological innovation.
Moreover, the combination of rising nutritional awareness, biotechnological advancement, and sustainability trends ensures that riboflavin will remain a cornerstone of the global nutrition and pharmaceutical ecosystem. Although challenges persist—ranging from supply chain dependencies to market competition—the overall outlook for the riboflavin market is remarkably optimistic.
Ultimately, riboflavin represents not only a nutrient but also a symbol of the global shift toward preventive healthcare, sustainable production, and conscious consumerism. Its influence will undoubtedly continue to grow, reinforcing its importance in shaping the future of nutrition and wellness worldwide.